Schedule a Consultation
216-480-4620Schedule a Consultation
216-480-4620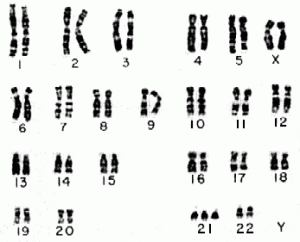
Chorionic villus sampling is the prenatal testing of a developing baby’s genetics. Doctors extract a sample from a section of the placenta (the chorionic villus), usually between 10 and 12 weeks of age. It can detect over 200 genetic and chromosomal disorders, including Down Syndrome, trisomy 13, cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell, and Tay-Sachs disease. It is over 99% accurate in detecting these conditions.
This is an important part of the genetic counseling services offered to expectant parents. It should typically be offered when:
Parents are under no obligation to have this testing performed. Parents will sometimes decline this testing if they know that they will not terminate a pregnancy regardless of the outcome. Other parents, even if they will not terminate a pregnancy, may choose find out in order to have more time to prepare in the event that the child is born with special needs. Other parents may want to find out early on whether their child has a serious and debilitating medical condition so that they can lawfully end the pregnancy.
As with any procedure, doctors should inform their patients of the risks of chorionic villus sampling. Informed consent discussions should include the possibility of a miscarriage (0.5% to 1.0%), infection, and oligohydramnios caused by leaking amniotic fluid, and malformed or underdeveloped limbs. Parents who are not advised of these risks may have the right to file lawsuits for failure of informed consent if the experience one of these complications.
There are several other methods that can be used to determine if a baby is going to born with medical problems. An amniocentesis can usually be performed between 16 and 22 weeks. It involves the removal by needle of a small amount of amniotic fluid from the womb. That fluid can then be tested. Ultrasounds can often diagnose structural problems, for example holoprosencephaly.
Depending on the state, parents may have a claim for wrongful birth or wrongful life if their health care providers act negligently by:
In these types of lawsuits, the parent or the child claims that, had information about the child’s medical condition been known, the parents would have lawfully aborted the pregnancy. The types of damages recoverable vary by state, but often include the unusual and extraordinary costs of medical care caused by the child’s medical condition.
Pregnancy can be a scary time, and most parents wonder if their children will have any significant medical injuries. Doctors can perform many tests to help answer those questions, and they should typically explain to parents their choices. If your child was born with genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, contact our birth injury lawyers at (440) 252-4399, or send us a message through our website.

